Layout of Simple Circular Curve :
The typical layout of simple circular curve is shown in the figure below.

R = Radius of Circular Curve
BC = Beginning of Curve
(or PC = Point of Curvature)
EC = End of Curve
(or PT = Point of Tangency)
PI = Point of Intersection
T = Tangent Length
(T = PI – BC = EC – PI)
L = Length of Curvature
(L = EC – BC)
M = Middle Ordinate
E = External Distance
C = Chord Length
Δ = Deflection Angle
Circular Curve Components

Properties of Circular Curve:
Degree of Curvature:
Traditionally, the “steepness” of the curvature is defined by either the radius (R) or the degree of curvature (D).
Degree of curvature = angle subtended by an arc of length 100 feet.
The diagram below is showing the degree of curvature.
If the arc length is 100 feet then the angle will be the degree of curvature as shown in the figure below.
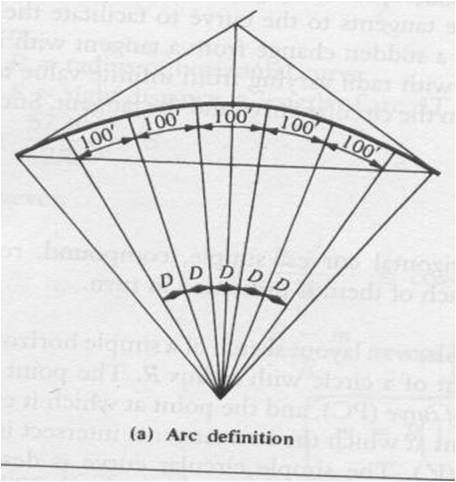
Steepness of curve can be defined in term of radius as shown in the figure below.
R = 5730 / D
(Degree of curvature is not used with metric units because D is defined in terms of feet.)
Length of Curve:
For a given external angle (Δ), the length of curve (L) is directly related to the radius (R).
L = (RΔπ) / 180
As we know π / 180=1/57.3
L = RΔ / 57.3
Where
R = Radius of Circular Curve
L = Length of Curvature
Δ = Deflection Angle
Conclusion :
From the above relation L = RΔ / 57.3 . It is concluded that larger the radius of curve longer will be the curve.
Other Formulas for the Layout of Simple Circular Curve :

Tangent: T = R tan(Δ/2)
Chord: C = 2R sin(Δ/2)
Mid Ordinate: M = R – R cos(Δ/2)
External Distance: E = R sec(Δ/2) – R
Circular Curve Geometry :

thankyou very much such article really help us just a night beforebefore xam………….
You are Welcome … Best of luck for your exam :)))
thank you now i can finish my assignment
I always emailed this web site post page to all my contacts,
for the reason that if like to read it then my links will too.