Cross section of road
Cross section of road consists of
- Carriage way.
- Shoulders and
- Right of way.
Carriage way
The metal portion (TST or carpeted) which is used for the smooth movement of the vehicles is known as carriage way.
Cross section of urban road
Foot path or side walk is added in the cross section in addition to the cross section of general road.
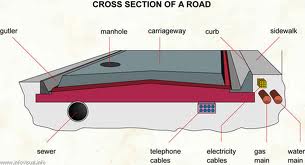
Foot path of side walk is the passage for the pedestrians.
Parallel strips along with the carriage way in urban road along with the carriage way throughout the road.
Requirements of foot path:
- It Must be neat clean.
- It Must be level.
- It must be Free from obstacles.
- Minimum recommended width is 4 feet.
Curb
The dividing line of carriage way and foot path is known as curb. Curb helps in the drainage purpose.
Types of kerbs
Mountable curb
The curb in which there is a certain slope is known as mountable curb. Its recommended height is 6 inches. It is helpful for easy parking as it is a slide so the cars can easily park over there.
Barrier curb
The curb whose height is above 6 inches is known as barrier curb. It does not help in parking. It is used in under passes and fly overs where we do not want parking.
Factors affecting road width
Factors upon which the width of carriage way depends are:
Speed of vehicles
If the speed of vehicles are high then the width of the road will be more. And if the speed of the vehicles are slow then the width will be less.
Dimensions or types of vehicles
Dimensions or types of vehicles moving on the carriage way ( LTV or HTV). The standard recommended width of the vehicles is 8 feet.
Road width also depends upon types of shoulders
Traffic volume
If greater volume of traffic, then width of the road will be kept more. Maximum recommended volume of traffic is 400 vehicles / hour then the width of carriage way is 12 feet. The carriage way is recommended as a dual carriage way.
Road width also depends upon condition of shoulders.
Leave a Reply