Typical components of road Pavement system
Several elements make up the roadway. Each layer represents one of the elements of the road pavement system. All these elements work together to provide a quality durable road pavement.
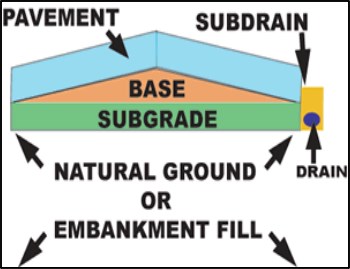
Embankment
When roads are built higher than the surrounding ground, a structure of compacted earth called an embankment is built.
The embankment is built to support the other three layers of the road pavement system. The construction of embankments for roadways can take up a large part of the total cost. Embankments can be made from almost any common type of deposit except topsoil.
Sub-grade
The sub-grade is made of soils that have been specially prepared to meet the requirements to support the other two layers.
The sub-grade is a selected soil material that is carefully compacted to provide uniform support to the pavement. The sub-grade lies directly on either the embankment or the native soil.
Base
The base is a mixture of crushed rock.
The base layer provides uniform support to the road pavement. It allows water that penetrates any joints or cracks in the road pavement to move quickly to the sub-drain without saturating and softening the sub-grade. The base layer lies directly on top of the sub-grade and is built of clean sand or rock.
Pavement
The top layer is the pavement.
The pavement materials can either be Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) and Portland Cement Concrete (PCC).
The pavement itself resists bending, and distributes vehicle weights over a large area.
Sub-Drain
The sub-drain collects water from the base and the sub-grade and drains that water into the ditch.
The sub-drain sits alongside the pavement, base and sub-grade. The sub-drain is basically a trench with a perforated pipe near the bottom. It is surrounded by clean coarse-size rock which allows rapid transportation of water.


Leave a Reply