Drag Force
When there is relative motion between the body and the fluid and the body is completely immersed in a homogeneous fluid , then the body may be subjected to two forces.
If the force is parallel to the motion then it is called drag.
The drag force on a submerged body can be viewed as having two components.
- Pressure drag force.
- Friction or surface drag.
Lift Force
If the force is normal to the relative motion of the body and the fluid in a homogeneous fluid, then it is called lift force.
Pressure on a body immersed in a moving liquid
When a solid body is held in the path of a moving fluid and is completely immersed in it, the body will be subjected to some pressure or force. Conversely, if a body is moving with a uniform velocity through a fluid, then fluid will exert some resistance to moving body, or the body has to exert some force to maintain steady movement.
A little consideration will show that if the plate or body is immersed in a liquid parallel to the direction of flow, it will experience less force as compared to the position when plate is held at right angle to the direction of flow.
It has been experimentally found that when a plate is held at some angle with the direction of the flow, the streamlines of the liquid gets deflected.
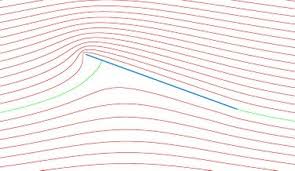
The pressure exerted by the streamlines is the same when the fluid is at rest and the body is moving uniformly through it or the body is at rest and fluid moves through it.
When the plate is held at some angle, it is subjected to some pressure. As this pressure is acting at right angle to the plate. So it will have two components.
- In the direction of the flow of the liquid which is called drag.
- At right angle to the flow of liquid which is called lift.
Leave a Reply